Upgrade to OpenREM 0.10.0 from 0.7.3 or later
Upgrades to OpenREM 1.0 can only be made from version 0.10.0. Installations earlier than that need to be updated to version 0.10.0 before updating to version 1.0.
These instructions can be used to upgrade any database from version 0.7.3 or later. 0.7.3 was released in August 2016. For upgrades from versions earlier than that, please review the upgrade instructions for that version in the 0.10.0-docs.
Upgrade preparation
Python 2.7.9 or later must be installed, but it must still be Python 2.7 and not any of the Python 3 releases.
To check the Python version, activate the virtualenv if you are using one, then:
$ python -V
If the version is earlier than 2.7.9, then an upgrade is needed. If the version is 3.x, then Python 2.7 must
be installed.
Ubuntu Linux
Check which version of Ubuntu is installed (
lsb_release -a)If it is 14.04 LTS (Trusty), then an operating system upgrade or migration to a new server is required. If migrating, ensure the version of OpenREM installed on the new server is the same as the one on the old server, then Database restore following the instructions and when up and running again perform the upgrade on the new server
16.04 LTS (Xenial) or later should have 2.7.11 or later available.
For other Linux distributions check in their archives for which versions are available.
Windows
A newer version of Python 2.7 can be downloaded from python.org and installed over the current version.
Linux and Windows
With a version of Python 2.7.9 or later, setuptools can be updated (activate virtualenv if using one):
$ pip install setuptools -U
Upgrade
Back up your database
For PostgreSQL on linux you can refer to Database backup
For PostgreSQL on Windows you can refer to Windows installations
For a non-production SQLite3 database, simply make a copy of the database file
Stop any Celery workers
Consider temporarily disabling your DICOM Store SCP, or redirecting the data to be processed later
If you are using a virtualenv, activate it
Install specific versions of some packages that are needed:
$ pip install django-crispy-forms==1.8.1
$ pip install django-solo==1.1.5
$ pip install flower==0.9.5
Install specific version of Celery:
Linux server:
$ pip install celery==4.2.2
Windows server:
D:\>pip install celery==3.1.25Install the new version of OpenREM:
$ pip install openrem==0.10.0
Update the configuration
Locate and edit your local_settings file
Ubuntu linux:
/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/openrem/openremproject/local_settings.pyOther linux:
/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/openrem/openremproject/local_settings.pyLinux virtualenv:
vitualenvfolder/lib/python2.7/site-packages/openrem/openremproject/local_settings.pyWindows:
C:\Python27\Lib\site-packages\openrem\openremproject\local_settings.pyWindows virtualenv:
virtualenvfolder\Lib\site-packages\openrem\openremproject\local_settings.py
Add additional log file configuration - changed with 0.8
Add the new extractor log file configuration to the local_settings.py - you can copy the ‘Logging
configuration’ section here if you haven’t made any changes. The addition that needs to be inserted are the
lines relating to the extractor log file. This is only for upgrading the database - the local_settings.py
file will be updated again for the upgrade to 1.0:
# Logging configuration
# Set the log file location. The example places the log file in the media directory. Change as required - on linux
# systems you might put these in a subdirectory of /var/log/. If you want all the logs in one file, set the filename
# to be the same for each one.
import os
LOG_ROOT = MEDIA_ROOT
logfilename = os.path.join(LOG_ROOT, "openrem.log")
qrfilename = os.path.join(LOG_ROOT, "openrem_qr.log")
storefilename = os.path.join(LOG_ROOT, "openrem_store.log")
extractorfilename = os.path.join(LOG_ROOT, "openrem_extractor.log")
LOGGING['handlers']['file']['filename'] = logfilename # General logs
LOGGING['handlers']['qr_file']['filename'] = qrfilename # Query Retrieve SCU logs
LOGGING['handlers']['store_file']['filename'] = storefilename # Store SCP logs
LOGGING['handlers']['extractor_file']['filename'] = extractorfilename # Extractor logs
# Set log message format. Options are 'verbose' or 'simple'. Recommend leaving as 'verbose'.
LOGGING['handlers']['file']['formatter'] = 'verbose' # General logs
LOGGING['handlers']['qr_file']['formatter'] = 'verbose' # Query Retrieve SCU logs
LOGGING['handlers']['store_file']['formatter'] = 'verbose' # Store SCP logs
LOGGING['handlers']['extractor_file']['formatter'] = 'verbose' # Extractor logs
# Set the log level. Options are 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARNING', 'ERROR', and 'CRITICAL', with progressively less logging.
LOGGING['loggers']['remapp']['level'] = 'INFO' # General logs
LOGGING['loggers']['remapp.netdicom.qrscu']['level'] = 'INFO' # Query Retrieve SCU logs
LOGGING['loggers']['remapp.netdicom.storescp']['level'] = 'INFO' # Store SCP logs
LOGGING['loggers']['remapp.extractors.ct_toshiba']['level'] = 'INFO' # Toshiba RDSR creation extractor logs
Migrate the database
In a shell/command window, move into the openrem folder:
Ubuntu linux:
/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/openrem/Other linux:
/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/openrem/Linux virtualenv:
vitualenvfolder/lib/python2.7/site-packages/openrem/Windows:
C:\Python27\Lib\site-packages\openrem\Windows virtualenv:
virtualenvfolder\Lib\site-packages\openrem\
python manage.py makemigrations remapp
python manage.py migrate remapp
Systemd service names in Ubuntu installs
Systemd service files were renamed in the the 0.9.1 docs to use openrem-function rather than function-openrem. To
update the service files accordingly, follow the following steps. This is optional, but will make finding them
easier (e.g. sudo systemctl status openrem-[tab][tab] will list them) and these names are assumed for the
Upgrade to Docker and Upgrading a native Linux install docs. However, only the gunicorn service remains after the upgrade to
1.0, so you may find it easier just to remember the only service names, or just rename that one.
sudo systemctl stop gunicorn-openrem.service
sudo systemctl stop celery-openrem.service
sudo systemctl stop flower-openrem.service
sudo systemctl disable gunicorn-openrem.service
sudo systemctl disable celery-openrem.service
sudo systemctl disable flower-openrem.service
sudo mv /etc/systemd/system/{gunicorn-openrem,openrem-gunicorn}.service
sudo mv /etc/systemd/system/{celery-openrem,openrem-celery}.service
sudo mv /etc/systemd/system/{flower-openrem,openrem-flower}.service
sudo systemctl enable openrem-gunicorn.service
sudo systemctl enable openrem-celery.service
sudo systemctl enable openrem-flower.service
sudo systemctl start openrem-gunicorn.service
sudo systemctl start openrem-celery.service
sudo systemctl start openrem-flower.service
Upgrade to 1.0
Now return to Installation instructions to follow the instructions to 1.0 for your preferred server solution.
After upgrading to version 1.0, there will be automatic tasks that are created to populate the summary fields introduced in version 0.10.
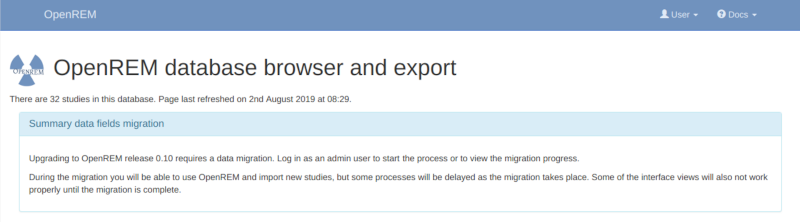
Log in as an administrator to start the migration process. If you have a large number of studies in your database this can take some time. A large database (several hundred studies) on slow disks might take a day or two, on faster disks or with a smaller database it could take from a few minutes to an hour or so. You will be able to monitor the progress on the home page as seen in the figure at the bottom of this page.
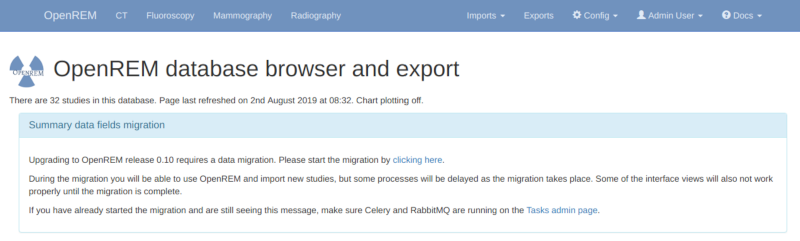
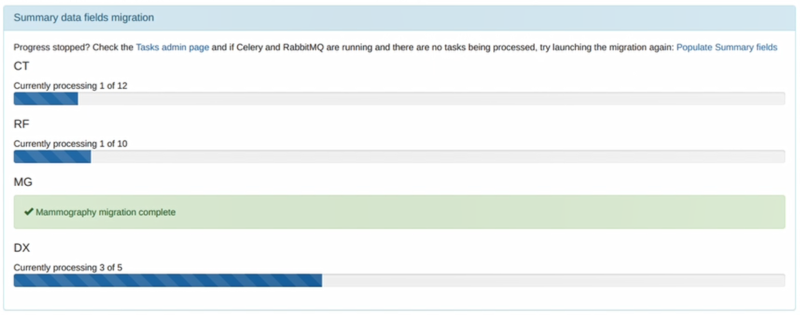
One task per modality type (CT, fluoroscopy, mammography and radiography) is generated to create a task per study in
each modality to populate the new fields for that study. If the number of workers is the same or less than the number
of modality types in your database then the study level tasks will all be created before any of them are executed as
all the workers will be busy. Therefore there might be a delay before the progress indicators on the OpenREM front
page start to update. You can review the number of tasks being created on the Config -> Tasks page.
Before the migration is complete, some of the information on the modality pages of OpenREM will be missing, such as the dose information for example, but otherwise everything that doesn’t rely on Celery workers will work as normal. Studies sent directly to be imported will carry on during the migration, but query-retrieve tasks will get stuck behind the migration tasks.
When the process is complete the ‘Summary data fields migration’ panel will disappear and will not be seen again.